Colour FAQs

Polymer Recycle
What is a Cube Blend?
A cube blend, also referred to as a salt & pepper mix, is a proportional mix that combines a masterbatch and natural polymer into a ready-to-use package. Color consistency and quality is ensured by SUGOI Polymers and the processor avoids steps related to blending or metering accuracy. One of the main advantages compared to precolored resin is that the majority of the polymer has not been previously melted by compounding, thus preserving its original properties.
What is the difference between a masterbatch and precolored resin?
A masterbatch is pre-dispersed concentrated color that is let down with natural polymer during molding. With a precolor all the polymer is entirely compounded with the proper amount of color and delivered ready-to-use, eliminating metering and dispersion difficulties. A masterbatch offers economic advantages associated with resin purchasing and color obsolescence. Additionally, since masterbatches are not fully compounded most of the polymer used does not exhibit an additional heat history, potentially deteriorating the properties of some polymers.
What is a masterbatch?
A masterbatch, also referred to as a concentrate, is a package for coloring plastics. Pigments, dyes, or other additives are dispersed into a polymer carrier which is extruded and pelletized. Those pellets are metered, or let down, into natural polymer, using a predefined ratio, during the molding process where additional mixing colors the resin entirely. Normal addition rates vary from 1 to 4%.
Understanding Plastic Recycling
Plastic recycling is the process of recovering scrap or waste plastic and reprocessing the material into useful products.
Since plastic is non-biodegradable, recycling is a part of global efforts to reduce plastic in the waste stream, especially the approximately eight million metric tonnes of waste plastic that enter the Earth’s ocean every year. This helps to reduce the high rates of plastic pollution.
Plastic recycling includes taking any type of plastic, sorting it into different polymers and then chipping it and then melting it down into pellets. After this stage, it can then be used to make items of any sort such as plastic chairs and tables.
Soft Plastics are also recycled such as polyethylene film and bags. This closed-loop operation has taken place since the 1970s and has made the production of some plastic products amongst the most efficient operations today.
What is Plastic made from?
Atomic structure of Plastics
Plastics are derived from materials found in nature, such as natural gas, oil, coal, minerals and plants.
The very first plastics were made by nature—did you know that rubber from a rubber tree is actually a plastic?
Interest in making plastics arose in the 1800s to replace scarce materials such as ivory and tortoise shell. The first synthetic plastics were derived from cellulose, a substance found in plants and trees. Cellulose was heated with chemicals and resulted in a new material that was extremely durable.
The raw materials for today’s plastics come from many places (some even use salt!), but most plastics can be made from the hydrocarbons that are readily available in natural gas, oil and coal.
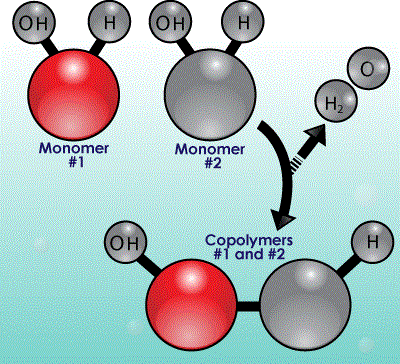
What is Compounding?
Compounding Process
SUGOI Enterprises compounds a wide range of engineering thermoplastics. Compounding is a process of melt blending plastics with other additives. This process changes the physical, thermal, electrical or aesthetic characteristics of the plastic. The final product is called a compound or composite.
Compounding starts with a base resin or polymer. SUGOI Enterprises has experience with various resin systems, each of which has unique characteristics that make it suitable for use in certain applications.
By incorporating an extensive range of additives, fillers, and reinforcers, a wide range of properties can be achieved in conductivity, flame retardance, wear resistance, structural, and precolored.
Our engineers independently select the additives based on your unique performance criteria. For example, glass fibers can be added at various levels to increase stiffness in a resin that is more flexible than desired.
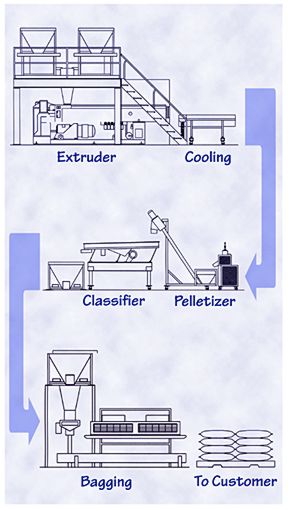
Compounding is done in several steps. Resin and additive(s) are fed through an extruder where they are combined. The melted compound exits the extruder in strands about the diameter of yarn. These strands are cooled and cut into pellets.
The pellets are thoroughly inspected and must pass 10 internal quality checks before being delivered to customers for use in injection molding or sheet extrusion.
Which plastics are safest?

Are-Plastics-safe
While it is a hard fact that people really try to avoid Plastics in their personal life as much as possible.
But it should be known that not all plastic is created equally.
Some readily leech extremely harmful chemicals while others have slower leaching rates and (comparatively) more innocuous chemical compositions.
The recycling codes which are little numbers inside the triangle made with arrows most often found on the bottom of a plastic product — designate which plastics are more toxic and which are safer.
What is Plastic Extrusion?
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation.

Plastic Extrusions Products
This process starts by feeding plastic material (pellets, granules, flakes or powders) from a hopper into the barrel of the extruder. The material is gradually melted by the mechanical energy generated by turning screws and by heaters arranged along the barrel.
The molten polymer is then forced into a die, which shapes the polymer into a pipe that hardens during cooling.
Whether it’s one hundred yards of pipe-tubing or a thousand Crazy Straws, plastic extrusion is in frequent use in today’s plastics industry because it’s readily available and easy to work with. The plastic extrusion process involves melting plastic material, forcing it into a die to shape it into a continuous profile, and then cutting it to length.
The process is a good choice for applications that require a final product with a constant cross-section. The low cost and high production rates make it a common manufacturing choice for products such as piping, plastic sheeting, weather stripping, wire insulation and adhesive tape.
